Description
What is Female Breast Anatomy?
Each breast has a number of sections (lobules) that branch out from the nipple. Each lobule holds tiny, hollow sacs (alveoli). The lobules are linked by a network of thin tubes (ducts). If you’re breast-feeding, ducts carry milk from the alveoli toward the dark area of skin in the center of the breast (areola). From the areola, the ducts join together into larger ducts ending at the nipple.
Oxygen and nutrients travel to breast tissue through the blood in your arteries and capillaries — thin, fragile blood vessels.
Spaces around the lobules and ducts are filled with fat, ligaments and connective tissue. The amount of fat in your breasts largely determines their size.
What is the Role of fats in Breast Size?
The volume and shape of the breasts are determined by the quantities of glandular and adipose tissue that they contain.
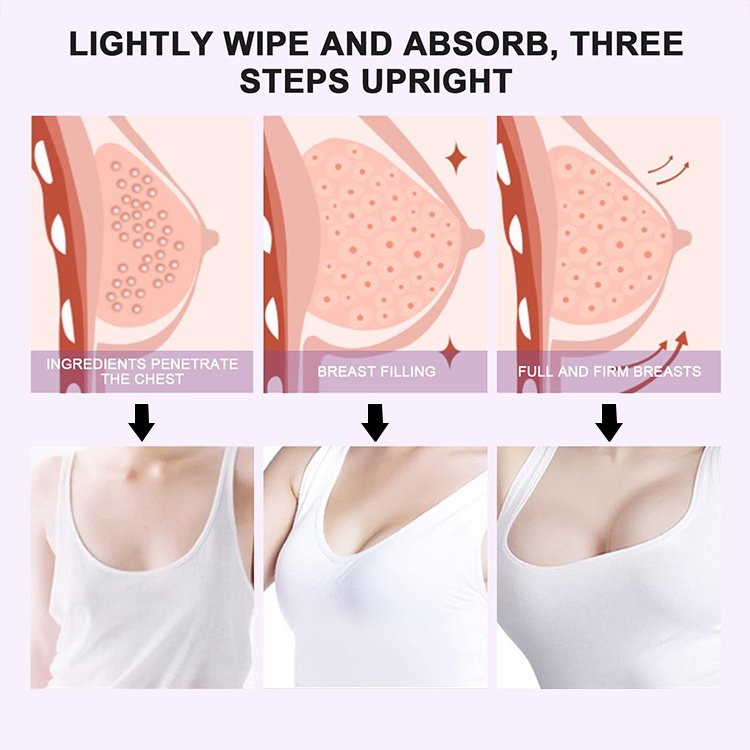
The subcutaneous fat that forms an external mantel over the mammary gland is a potential target for amplifying the curvature of the breasts and restoring the shapeliness of the décolleté.
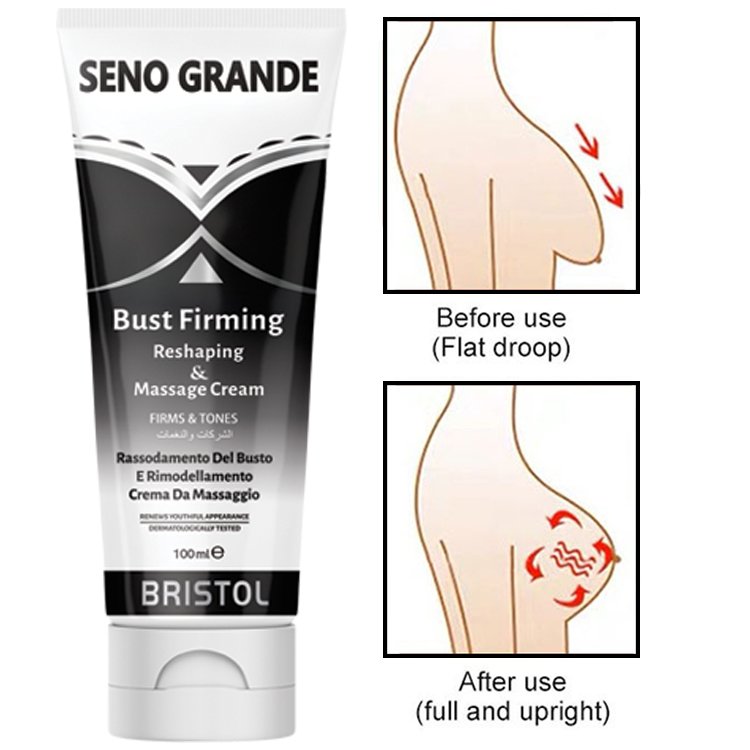
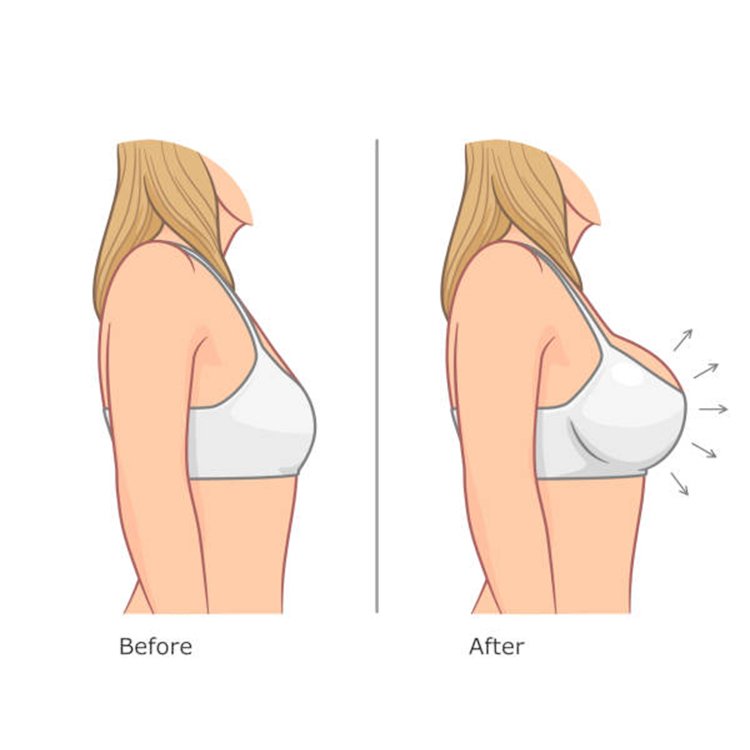
What is Sagging Breast?
Drooping of the breast tissue is scientifically referred to as “breast ptosis.”
Multiple factors increase the risk of sagging breasts.
Sagging breasts is a naturally occurring phenomenon that happens with age.
However, there may still be a lot of shame and insecurity around the issue.
What Causes Sagging Breasts?
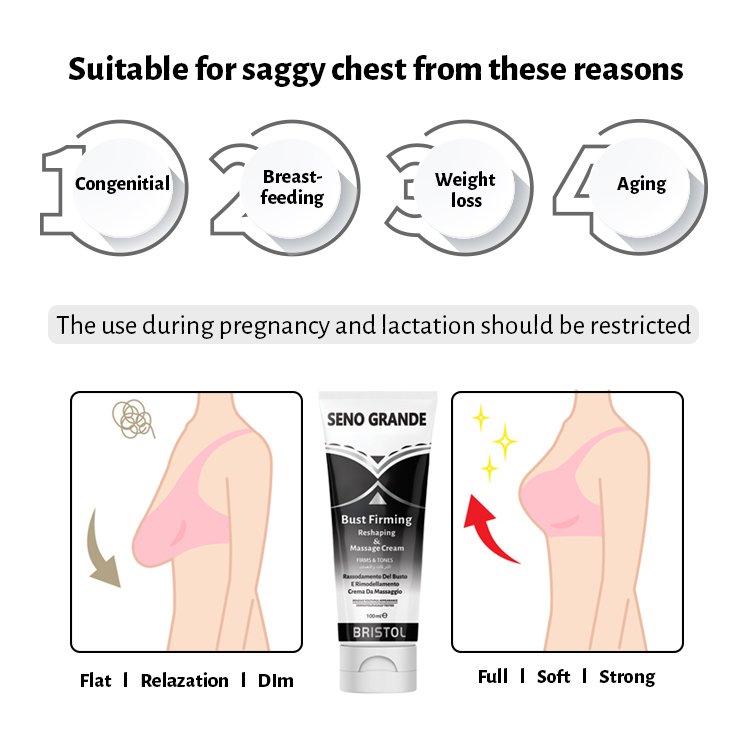
Sagging breasts can be caused by a combination of the following,
• Pregnancy
• Menopause
• The breakdown of the mammary glands
• A decrease in the elasticity of the skin
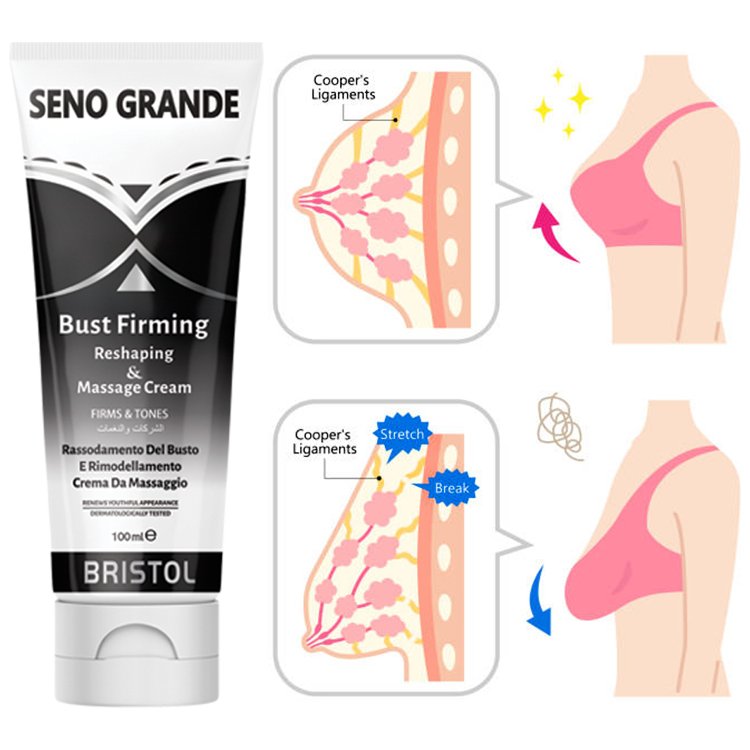
• Weakened breast ligaments, called Cooper’s ligament
• Gravity
Various factors can affect including age, the size of your breasts, and smoking.















35 reviews for Seno Grande Bust Firming Cream
There are no reviews yet.